An Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) serves as the foundation for aligning sales and marketing efforts, enabling businesses to target high-value accounts with precision. Developing a robust ICP goes beyond surface-level insights. It involves leveraging data analysis, market research, and customer feedback to create a comprehensive blueprint of your best-fit customers. While this process may seem complex, the benefits are undeniable—streamlined workflows, personalized strategies, and higher ROI. In this article, we delve into the pivotal role of ICPs in modern B2B strategies, their advantages, a step-by-step guide to building one, and their impact on achieving sustainable results in 2025 and beyond.
What is an Ideal Customer Profile?
An Ideal Customer Profile is a detailed description of the type of company that is the perfect fit for your products or services. In B2B and account-based marketing (ABM), the ICP framework helps define which companies are most likely to benefit from your offering and become long-term, profitable customers. It typically includes key characteristics such as industry, company size, revenue, location, and specific business needs. The ideal customer profile framework serves as a foundational guide to help identify the best solution to know your ICP through target audience and target companies that align most closely with your offerings.
The ICP companies serve as a guide for sales and marketing teams, enabling them to focus on leads that have the highest potential for success. It allows you to prioritize resources on accounts that align with your strengths, ensuring that time and effort are not wasted on unqualified prospects. Factors like legal conflicts, location restrictions, and time requirements also play a role in shaping ICP marketing, ensuring that your target customers are not only a good fit but also accessible.
By identifying the ideal customer, businesses can avoid chasing leads that aren’t likely to convert, reducing churn and increasing overall efficiency. One of the ideal customer profile example, businesses may identify certain customer types, such as startups with limited budgets, and adjust their approach to focus on more suitable prospects. This leads to higher win rates, larger deals, and better long-term customer relationships.
Why is Knowing Your ICP Crucial?
Defining your ideal customer profile is essential for driving success in B2B marketing, sales, and brand building. Understanding your ICP enables better resource allocation by allowing your team to focus on prospects most likely to convert. By targeting the right customers, businesses can streamline B2B lead generation and consistently meet sales targets. A strong ICP framework aligns the sales approach with customer needs, significantly improving the likelihood of closing deals. By concentrating efforts on ideal-fit customers, sales teams can drive consistent results and avoid wasted resources. Additionally, with an ICP in marketing, businesses can adopt a value-based pricing strategy, tailoring their solutions to meet the specific needs of targeted prospects. This not only boosts the average deal size but also reduces churn. As per the ideal customer profile example, SuperOffice saw a significant increase in deal size and customer retention after refining its ideal customer profile. Furthermore, an ICP framework helps identify high-value, scalable customers, enabling businesses to focus on accounts with the greatest growth potential. By leveraging customer insights, businesses can gain a competitive advantage and achieve sustainable growth. Ultimately, knowing your ideal customer profile improves alignment across teams, accelerates conversions, and enhances customer lifetime value, ensuring long-term success and profitability.
Ideal Customer Profile Vs Buyer Personas
The primary difference between an ideal customer profile and a buyer persona lies in their scope and application. A target ICP defines the characteristics of the ideal customer for a business, typically at the company level. It outlines broad traits like industry, company size, revenue, and geographic location, helping businesses target the right types of organizations. The ideal customer profile is a strategic framework used to identify potential customers that would benefit most from a business’s offerings. The ideal customer profile framework plays a key role in setting this strategy.
Conversely, a buyer persona delves deeper, focusing on individual customers within the ICP framework. It is a semi-fictional representation of a customer archetype, detailing specific attributes such as demographics, goals, challenges, buying behaviors, motivations, and pain points. Buyer personas provide a more granular, human touch, allowing businesses to craft personalized marketing and sales strategies tailored to these personas’ unique needs and preferences.
While an ICP persona is used at the top of the sales funnel to qualify leads and prioritize accounts, buyer personas are leveraged throughout the sales and marketing process to guide content creation, messaging, and customer interactions. In B2B settings, businesses might create multiple buyer personas for different decision-makers within a target account. ICP defines who to target, while buyer personas outline how to communicate with and engage individuals within those organizations. Both tools complement each other, helping businesses align their strategies with customer needs and drive more effective marketing and sales efforts.
Types of Customer Profiles
Developing an ideal customer profile is essential for ensuring that these strategies address the specific needs and preferences of your target audience. Here are four key types of customer profiles:
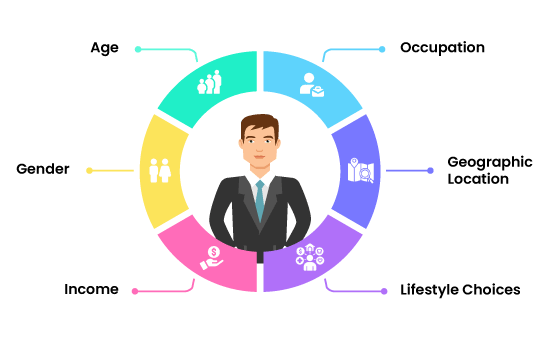
Demographic profiling: This is one of the simplest forms of customer segmentation, focusing on basic personal characteristics such as age, gender, income, education level, marital status, and occupation. While these characteristics alone may not provide a comprehensive understanding, they serve as a foundation for identifying broader trends within target audiences. By integrating these insights into an ideal customer profile, businesses can better align their communication strategies with customer needs.
Geographic profiling: Geographic profiling analyzes the location of customers, considering factors like climate, culture, and regional preferences. This helps businesses understand how geographic location influences consumer behavior and purchasing habits. For example, products or messages that resonate in urban areas may need adaptation when targeting rural areas. A well-constructed ideal customer profile incorporates geographic details to refine marketing efforts further and enhance their relevance to diverse audience segments.
Psychographic profiling: Psychographic profiling goes beyond basic demographics, focusing on the motivations, attitudes, values, and lifestyle choices of customers. It helps businesses connect emotionally with their audience by appealing to their personal beliefs and interests. An ideal customer profile that incorporates psychographic data enables businesses to better track changes in consumer priorities, like an increased focus on sustainability or value for money.
Behavioral profiling: Behavioral profiling examines how customers interact with a brand, including buying patterns, frequency of purchases, and the channels they engage with. By aligning this data with an ideal customer profile, businesses can better understand customer loyalty, purchasing behavior, and potential areas for upselling or cross-selling. Mapping customer behavior throughout the buying journey helps anticipate needs, reduce churn, and improve the overall customer experience, all while ensuring alignment with the characteristics of the ICP.

Methods of Customer Profiling
Ideal customer profile involves segmenting customers into groups based on shared characteristics, goals, and behaviors to better understand their preferences and needs. This segmentation helps businesses create tailored marketing strategies and enhance customer experiences. Below are three key methods of customer profiling:
1. Personality Traits
The personality traits delve into customers’ lifestyles, values, interests, and social class to identify distinct market segments. Lifestyle factors like age, gender, and location influence how products fit into customers’ routines, such as school, college, or office life.
Values and social upbringing also play a significant role in purchasing behavior. A customer’s attitude towards spending and their income level, which defines their social class, determine their buying power. Psychographic profiling requires tools like surveys, interviews, and website analytics to gather insights into personal preferences.
2. Consumer Typology Profiling
Loyal consumers are deeply committed to a brand, often serving as brand advocates who promote their preferred products through word-of-mouth. Discount consumers prioritize savings over brand loyalty, making purchases primarily when there are discounts or sales available. Impulsive consumers are emotionally driven shoppers who make spontaneous purchases without specific goals, often acting on immediate desires rather than logical decisions. In contrast, need-based consumers are practical buyers who shop only to fulfil specific needs, focusing on efficiency and purpose.
3. Characteristics Profiling
Characteristics profiling examines traits that influence customer decisions, such as convenience, connectivity, and personalization. Convenience-driven customers value quick and hassle-free experiences, often favoring online shopping for its speed. Connectivity-driven consumers prefer products that foster a sense of belonging or are recommended by peers. Personalization-driven buyers seek unique, customized experiences tailored to their specific needs. By analyzing these characteristics, businesses can build a more detailed ideal customer profile to target and serve their audience effectively.
How to Find Your Ideal Customer Profile?
Creating an Ideal Customer Profile involves analyzing data, identifying patterns, and tailoring strategies to target your ideal audience. By following these steps, you can develop a robust ideal customer profile that aligns your business efforts, streamlines teamwork, and drives growth.
Step 1: Analyze Existing Customers
Begin by studying your top-performing customers—those who are loyal, generate significant revenue and derive maximum value from your offerings. Collect data on their demographics, behavior, industry, company size, and purchasing patterns. Use CRM or ERP systems to pinpoint key performance indicators such as annual contract value (ACV) and customer lifetime value (CLTV). These insights help identify patterns and traits of your ideal customers.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Expand your understanding by conducting market research to identify trends and untapped customer segments. Utilize tools like industry reports, SWOT analyses, and social media monitoring. This will help uncover shared characteristics among potential customers, such as challenges, motivations, or purchasing triggers, aligning them with your target audience’s behavior.
Step 3: Define Pain Points and Value Propositions
Pinpoint the primary challenges your ideal customers face and align your product or service as the solution. Gather customer feedback through surveys, focus groups, and social listening. This step ensures that your ideal customer profile is not only accurate but actionable, emphasizing your ability to meet the customer’s specific needs.
Step 4: Segment and Categorize Data
Organize your data into meaningful attributes such as firmographics, technographics, and psychographics. Identify relevant details like company size, technological preferences, and organizational values. Categorizing data helps your sales and marketing teams tailor their strategies effectively to target specific segments.
Step 5: Document Ideal Customer Profile
Create a comprehensive document outlining your ideal customer profile. Include critical elements like demographic details, behavioral insights, pain points, and unique value propositions. Use client profile templates or worksheets to streamline the process. Regularly revisit and refine the document to incorporate evolving customer behaviors and new market insights.
Step 6: Validate and Leverage Your ICP
Test your ideal customer profile by aligning it with marketing campaigns, sales strategies, and product development efforts. Monitor performance metrics to validate its effectiveness. Use your ICP as a benchmark for lead scoring, personalized advertising, and discovering new market opportunities.
Tools to Create a B2B Ideal Customer Profile
To understand your customers and build a detailed customer profile, you can use a variety of tools that collect valuable data from different customer touchpoints. Here are eight major tools you can use to collect customer profile data:
Lead Capture Forms: Lead capture forms on your website allow you to gather basic customer information, such as name, email, and preferences, in exchange for incentives like discounts or exclusive content. By analyzing the data submitted through these forms, you can gain insights into what attracts visitors and tailor your marketing efforts accordingly, helping refine your ideal customer persona.
Surveys: Surveys sent to customers after they’ve used your product or service provide qualitative feedback. You can ask customers what they liked or disliked about your offerings, uncover areas for improvement, and identify opportunities for upselling or product development. This data strengthens customer relationships by showing you value their opinions.
Email Marketing Platforms: Email marketing platforms allow you to track customer interactions with your emails, such as open rates, click-through rates, and purchase behavior. This data helps you segment your audience more effectively and understand their interests. For instance, if a customer clicks on a product link in an email but doesn’t purchase, it could indicate an upselling opportunity.
Social Media: Social media platforms provide a wealth of information on how customers engage with your brand. Monitoring interactions like comments, shares, and likes can give you a sense of customer loyalty and interest. You can also use social media data to engage with customers directly, improving customer experience and fostering stronger relationships.
Customer Support Channels: Omnichannel customer support tools capture valuable interaction data across various touchpoints, such as email, live chat, and social media. By tracking conversation history, these tools help you understand customer issues, preferences, and feedback, enabling you to offer personalized support and build better relationships.

Google Analytics: Google Analytics provides in-depth insights into how customers interact with your website. You can track metrics like page views, bounce rates, and user flow, helping you understand which pages or products are most popular and how customers navigate through your site. This data informs your website optimization and marketing strategies.
Best Practices for Creating a B2B Ideal Customer Profile
Creating an ideal customer profile (ICP) is essential for aligning marketing and sales efforts with the right audience in your go-to-market strategy. By following these best practices, businesses can create an ICP in marketing that drives effective targeting, personalized messaging, and improved conversion rates.
Analyze your best customers: Start by examining your existing customer base to identify patterns. Focus on those who generate the most revenue, have the highest engagement, or exhibit the longest retention. Analyze their demographics, behaviors, and purchasing motivations to understand what makes them ideal and help shape your ideal customer persona.
Leverage data analytics: Use data from CRM tools, website analytics, and customer surveys to uncover insights about customer preferences and behaviors. Pay attention to trends in purchase history, geographic locations, and industry verticals. Data-driven insights help in making accurate and objective profiles that support your ideal customer profile framework.
Understand pain points and goals: Dive deep into the challenges your customers face and how your product or service solves them. Understand their goals and aspirations to position your offering as a solution that aligns with their needs. This ensures that your marketing ICP focuses on delivering value.
Segment by behavior and demographics: Demographics such as age, income, and location are foundational for profiling, but behavioral factors like buying patterns, product usage, and communication preferences provide additional depth. Segmenting by these factors creates a well-rounded profile that can drive personalized marketing strategies.
Validate and refine regularly: Customer preferences and market dynamics evolve. Periodically review and update your ICP to ensure it remains relevant. Engage with sales teams and customer feedback to refine the profile based on real-world interactions, keeping your ICP persona accurate and effective. By aligning efforts, you can boost your ICP through a brand-to-demand strategy and maintain a competitive edge.
What Are the Essential Data Points for a B2B Ideal Customer Profile?
Incorporating data points into a unified customer profile creates a comprehensive view that benefits marketing, sales, and support teams, leading to enhanced customer experiences and better business outcomes. Building an ideal customer profile (ICP) requires gathering essential data across three key areas:
Customer Marketing Data
Marketing teams can utilize consumer profiles to create marketing campaigns and predictive messaging. This data highlights buying behaviors, trends, and patterns. For instance, knowing which products a customer has previously returned helps avoid sending similar offers. Similarly, if a customer frequently opens emails about a specific product but doesn’t make a purchase, this signals interest that can be nurtured with additional information or follow-up.
Customer Sales Data
Sales teams benefit from customer profiles by gaining insights into potential upsell or cross-sell opportunities. The intent data helps sales reps assess the likelihood of a customer accepting an upgrade or purchasing a complementary product. For example, using tools like Zendesk, sales teams can track customer activity, such as past purchases or preferences, allowing them to approach customers with highly relevant offers and increase conversion rates.
Customer Support Data
Customer support teams use profiles to provide tailored service experiences. Detailed interaction histories, including previous issues and attempted solutions, help agents personalize their responses. This intent data ensures support teams avoid repeating solutions, resulting in faster, more effective service. For instance, if a customer has already tried certain solutions, support teams can recommend alternative approaches or escalate the issue as needed.
In conclusion, an ideal customer profile (ICP) is a crucial tool for businesses looking to optimize their sales and marketing efforts. By focusing on the customer most likely to derive value from your offerings, companies can boost conversion rates, minimize wasted resources, and improve ROI. Building an ideal customer profile requires thorough data analysis, market research, and a deep understanding of customer pain points. Continuously refining your ICP ensures that your business remains aligned with evolving market dynamics, driving sustainable success. In a competitive landscape, businesses that master their ICP will position themselves for optimal growth and lasting customer relations in 2025 and beyond.